ELB
Load Balancer CheatSheet
- Managed load balanding service and scales automatically
- distributes incoming application traffic across multiple EC2 instances
- is distributed system that is fault tolerant and actively monitored by AWS scales it as per the demand
- are engineered to not be a single point of failure
- need to Pre-Warm ELB if the demand is expected to shoot especially during load testing
- supports routing traffic to instances in multiple AZs in the same region
- Health Checks : to route traffic only to the healthy instances
- supports Listners with HTTP, HTTPS, SSL, TCP protocols
- has an associated IPv4 and dual stack DNS name
- Connect draining : to help complete the in-flight requests in case an instance is deregistered
- For High Availability : it is recommended to attach 1 subnet per AZ for 2 AZs, even if the instances are in a single subnet
- canNOT assign an Elastic IP adresses to an ELB
- IPv4 & IPv6 support
SSL
- SSL termination : can offload the work of encryption and decryption so that the EC2 instances can focus on their main work
- HTTP listener does NOT support Client Side Certificate
- SSL termination at backend instances/support for Client Side Certificate use TCP for connections from the client to the ELB, use the SSL protocol for connections from the ELB to the back-end application, and deploy certificates on the back-end instances handling requests.
- supports a single SSL certificate, so for multiple SSL certificate multiple ELBs need to be created
Cross Zone Load Balancing
- to help route traffic evenly across all EC2 instances regardless of the AZs they reside in
- to help identify client IP
- Proxy Protocol header for TCP/SSL connections
- X-Forward headers for HTTP/HTTPS connections
Stick Sessions (session affinity)
- to bind a user’s session to a specific application instance
- it is NOT fault tolerant : if an instance is lost, the information is lost
- requires HTTP/HTTPS listener and does NOT work with TCP
- requires SSL termination on ELB as it uses the headers
Feautures
- 3 types of Load Balancer
- Application Load Balancers for intelligent routing : distinguish traffic for different targets (mysite.co/accounts vs. mysite.co/sales vs. mysite.co/support) and distribute traffic based on rules for target group, condition, and priority.
- Network Load Balancers for very high performance or static IP, only L4
- Classic Load Balancers for low cost and don’t need any intelligence built in
- 504 Error : The gateway was timed out. The application not responding within the timeout period
- Trouble shoot the application. NOT ELB. Is it the Web Server or Database Server?
- For Classic Load Balancers, If you need the PUBLIC IPv4 address of your end user, look for the X-Forwared-For header
- Instances monitored by ELB are reported as; InService or OutofService
- Health Checks check the instance health by talking to it
- Load Balancers have their own DNS name. NOT IP
-
!!! Read ELB FAQ for Classic Load Balancers !!!
- Advanced Load Balancer Theory
- Sticky Sessions enable your users to stick to the same EC2 instance. Can be useful if you are storing information locally to that instance
- Cross Zone Load Balancing enables you to load balance across multiple availability zones
- Path patterns allow you to direct traffic to different EC2 instances based on the URL contained in the request ex) www.myurl.com -> EC2-01 / www.myurl.com/images -> EC2-02
- Target Group
Scenario
- There are many clients complaining that the online trading application of an investment bank is always down. Your manager instructed you to re-design the architecture of the application to prevent the unnecessary service interruptions. To ensure high availability, you set up the application to use an ELB to distribute the incoming requests across an auto-scaled group of EC2 instances in two single Availability Zones.
In this scenario, what happens when an EC2 instance behind an ELB fails a health check?- A) The ELB stops sending traffic to the EC2 instance
- When the load balancer determines that an instance is unhealthy, it stops routing requests to that instance. The load balancer resumes routing requests to the instance when it has been restored to a healthy state.
- You have a new e-commerce web application written in Angular framework which is deployed to a fleet of EC2 instances behind an Application Load Balancer. You configured the load balancer to perform health checks on these EC2 instances.
What will happen if one of these EC2 instances failed the health checks?- A) The Application Load Balancer stops sending traffic to the instance that failed its health check
- Each load balancer node routes requests only to the healthy targets. Each load balancer node checks the health of each target, using the health check settings for the target group with which the target is registered. After your target is registered, it must pass one health check to be considered healthy. After each health check is completed, the load balancer node closes the connection that was established for the health check.
- In Elastic Load Balancing, there are various security features that you can use such as Server Order Preference, Predefined Security Policy, Perfect Forward Secrecy and many others. Perfect Forward Secrecy is a feature that provides additional safeguards against the eavesdropping of encrypted data through the use of a unique random session key. This prevents the decoding of captured data, even if the secret long-term key is compromised.
Perfect Forward Secrecy is used to offer SSL/TLS cipher suites for which two AWS services?- A) CloudFront and Elastic Load Balancing
- CloudFront and Elastic Load Balancing are the two AWS services that support Perfect Forward Secrecy. SSL/TLS is commonly used when you have sensitive data travelling through the public network.
- You are helping out a new DevOps Engineer to design her first architecture in AWS. She is planning to develop a highly available and fault-tolerant architecture which is composed of an Elastic Load Balancer and an Auto Scaling group of EC2 instances deployed across multiple Availability Zones. This will be used by an online accounting application which requires path-based routing, host-based routing, and bi-directional communication channels using WebSockets.
Which is the most suitable type of Elastic Load Balancer that you should recommend for her to use?- A) Application Load Balancer
- Application Load Balancer : If you need flexible application management and Path based routing, host-based routing. HTTP(L7)
- Network Load Balancer : If extreme performance and static IP is needed for your application. TLS Termination. TCP/UDP(L4)
- Classic Load Balancer : If your application is built within the EC2 Classic network
- A travel company has a suite of web applications hosted in an Auto Scaling group of On-Demand EC2 instances behind an Application Load Balancer that handles traffic from various web domains such as
i-love-manila.com,i-love-boracay.com,i-love-cebu.comand many others. To improve security and lessen the overall cost, you are instructed to secure the system by allowing multiple domains to serve SSL traffic without the need to reauthenticate and reprovision your certificate everytime you add a new domain. This migration from HTTP to HTTPS will help improve their SEO and Google search ranking.
Which of the following is the most cost-effective solution to meet the above requirement?- A) Upload all SSL certificates of the domains in the ALB using the console
and bind multiple certificates to the same secure listener on your load balancer.
ALB automatically choose the optimal TLS certificate for each client using Server Name Indication(SNI) - SSL(Server Secure Layer) : SSL은 또한 웹 서버 인증, 서버 인증이라고 불리는데, 클라이언트와 서버 간의 통신을 제3자가 보증해주는 전자화된 문서다. 클라이언트가 서버에 접속한 직후에 서버는 클라이언트에게 이 인증서 정보를 전달한다. HTTPS SSL 프로토콜 위에서 돌아가는 프로토콜이다. 즉 HTTPS로 데이터 전송을 시작할 때, SSL이 데이터 보안을 제공한다.
- SNI Custom SSL relies on the SNI extension of the Transport Layer Security protocol, which allows multiple domains to serve SSL traffic over the same IP address by including the hostname which the viewers are trying to connect to.
You can host multiple TLS secured applications, each with its own TLS certificate, behind a single load balancer. In order to use SNI, all you need to do is bind multiple certificates to the same secure listener on your load balancer. ALB will automatically choose the optimal TLS certificate for each client. These features are provided at no additional charge. - Using a wildcard certificate : is incorrect because a wildcard certificate can only handle multiple sub-domains but not different domains.
- Adding a Subject Alternative Name (SAN) for each additional domain to your certificate : is incorrect because although using SAN is correct, you will still have to reauthenticate and reprovision your certificate every time you add a new domain.
- Create a new CloudFront web distribution and configure it to serve HTTPS requests using dedicated IP addresses in order to associate your alternate domain names with a dedicated IP address in each CloudFront edge location : is incorrect because although it is valid to use dedicated IP addresses to meet this requirement, this solution is not cost-effective. Remember that if you configure CloudFront to serve HTTPS requests using dedicated IP addresses, you incur an additional monthly charge. The charge begins when you associate your SSL/TLS certificate with your CloudFront distribution. You can just simply upload the certificates to the ALB and use SNI to handle multiple domains in a cost-effective manner.
- A) Upload all SSL certificates of the domains in the ALB using the console
- You are a Solutions Architect for a major TV network. They have a web application running on eight Amazon EC2 instances, consuming about 55% of resources on each instance. You are using Auto Scaling to make sure that eight instances are running at all times. The number of requests that this application processes are consistent and do not experience spikes. Your manager instructed you to ensure high availability of this web application at all times to avoid any loss of revenue. You want the load to be distributed evenly between all instances. You also want to use the same Amazon Machine Image (AMI) for all EC2 instances.
How will you be able to achieve this?- A) Deploy 4 EC2 instances with Auto Scaling in 1 Availability Zone and 4 in another availability zone in the same region behind an Amazon Elastic Load Balancer.
- Take note that Auto Scaling will launch additional EC2 instances to the remaining Availability Zone/s in the event of an Availability Zone outage in the region.
- the ELB is designed to only run in one region and not across multiple regions.
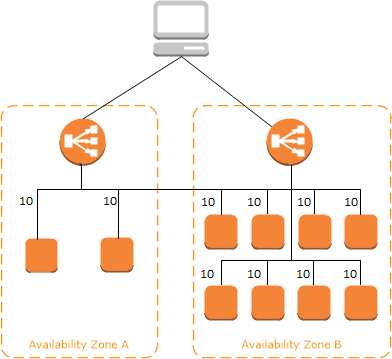
- In your VPC, you have a Classic Load Balancer distributing traffic to 2 running EC2 instances in
ap-southeast-1aAZ and 8 EC2 instances inap-southeast-1bAZ.
However, you noticed that half of your incoming traffic goes toap-southeast-1aAZ which over-utilize its 2 instances but underutilize the other 8 instances in the other AZ.
What could be the most likely cause of this problem?- A) Cross-Zone Balancing is disabled.
- Cross-zone load balancing reduces the need to maintain same numbers of instances in each enabled Availability Zone, and improves your application’s ability to handle the loss of one or more instances.
-
If cross-zone load balancing is enabled, each of the 10 targets receives 10% of the traffic. This is because each load balancer node can route its 50% of the client traffic to all 10 targets.
-
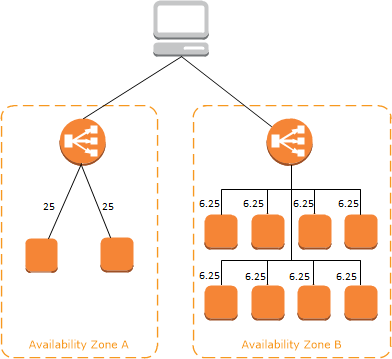
-
If cross-zone load balancing is disabled, each of the 2 targets in Availability Zone A receives 25% of the traffic and each of the 8 targets in Availability Zone B receives 6.25% of the traffic. This is because each load balancer node can route its 50% of the client traffic only to targets in its Availability Zone.
- A bank portal application is hosted in an Auto Scaling group of EC2 instances behind a Classic Load Balancer (CLB). You are required to set up the architecture so that any back-end EC2 instances that you de-register should complete the in-progress requests first before the de-registration process takes effect. Conversely, if a back-end instance fails health checks, the load balancer should not send any new requests to the unhealthy instance but should allow existing requests to complete.
How will you configure your load balancer to satisfy the above requirement?- A) Configure Connection Draining
- Connection Draining : To ensure that a Classic Load Balancer stops sending requests to instances that are de-registering or unhealthy while keeping the existing connections open
- Sticky Sessions : is incorrect because the sticky sessions feature is mainly used to ensure that all requests from the user during the session are sent to the same instance.
- Cross-Zone Load Balancing : is incorrect because Cross-Zone load balancing is mainly used to distribute requests evenly across the registered instances in all enabled Availability Zones.
- You are managing a global news website which has a very high traffic. To improve the performance, you redesigned the application architecture to use a Classic Load Balancer with an Auto Scaling Group in multiple Availability Zones. However, you noticed that one of the Availability Zones is not receiving any traffic. What is the root cause of this issue?
- A) The Availability Zone is not properly added to the load balancer which is why it is not receiving any traffic
- EC2-Classic에서 로드 밸런서를 설정하여 단일 가용 영역 또는 여러 가용 영역의 EC2 인스턴스에 수신 요청을 분산시킬 수 있습니다.
- 먼저 사용하려는 모든 가용 영역에서 EC2 인스턴스를 시작하십시오.
- 그런 다음 이러한 인스턴스를 로드 밸런서에 등록하십시오.
- 마지막으로 가용 영역을 로드 밸런서에 추가하십시오. 가용 영역을 추가하면 로드 밸런서가 해당 가용 영역에 등록된 인스턴스로 요청을 라우팅하기 시작합니다. 언제든지 로드 밸런서의 가용 영역을 수정할 수 있습니다.
- 기본적으로 로드 밸런서는 가용 영역 전체에 걸쳐 요청을 균등하게 라우팅합니다. 가용 영역에 등록된 인스턴스간에 요청을 균등하게 라우팅하려면 영역 간 로드 밸런싱(cross-zone load balancing)을 활성화하십시오.
- You are assigned to design a highly available architecture in AWS. You have two target groups with three EC2 instances each, which are added to an Application Load Balancer. In the security group of the EC2 instance, you have verified that the port 80 for HTTP is allowed. However, the instances are still showing out of service from the load balancer.
What could be the root cause of this issue?- A) The health check configuration is not properly defined
- 보안 그룹이 올바르게 구성되었으므로 대상 그룹(Target group)의 상태 확인 구성(health check configuration)이 잘못되어 문제가 발생할 수 있습니다.
- health check : Application Load Balancer는 주기적으로 요청을 등록된 대상으로 보내 상태를 테스트합니다. 이러한 테스트를 바로 상태 확인이라고 합니다. 로드 밸런서는 정상 상태 인스턴스로만 요청을 라우팅합니다. 인스턴스가 비정상 상태라고 판단되면 로드 밸런서는 이 인스턴스로의 요청 라우팅을 중지합니다. 인스턴스가 정상 상태로 복구가 되면 로드 밸런서는 이 인스턴스로의 요청 라우팅을 재개합니다.
- You have a web application hosted on a fleet of EC2 instances located in two Availability Zones that are all placed behind an Application Load Balancer. As a Solutions Architect, you have to add a health check configuration to ensure your application is highly-available.
Which health checks will you implement?- A) HTTP or HTTPS health check
- 여기에 언급 된 ELB 유형은 Application Elastic Load Balancer입니다. HTTP 및 HTTPS 트래픽이있는 웹 애플리케이션에 유연한 기능 세트를 원하는 경우에 사용됩니다. 반대로 HTTP 및 HTTPS의 두 가지 상태 확인 만 허용합니다.
- TCP 상태 확인은 다른 유형의 ELB 인 Network Load Balancer에서만 제공됩니다. 응용 프로그램에 초-고성능 및 고정 IP 주소가 필요한 경우에 사용됩니다.
- The social media company that you are working for needs to capture the detailed information of all HTTP requests that went through their public-facing application load balancer every five minutes. They want to use this data for analyzing traffic patterns and for troubleshooting their web applications in AWS.
Which of the following options meet the customer requirements?- A) Enable access logs on the application load balancer.
- Elastic Load Balancing은 로드 밸런서로 전송 된 요청에 대한 자세한 정보를 캡처하는 액세스 로그를 제공합니다. 각 로그에는 요청을 받은 시간, 클라이언트의 IP 주소, 대기 시간, 요청 경로 및 서버 응답과 같은 정보가 포함됩니다. 이러한 액세스 로그를 사용하여 트래픽 패턴을 분석하고 문제를 해결할 수 있습니다.
- 액세스 로깅은 Elastic Load Balancing의 선택적 기능이며 기본적으로 비활성화되어 있습니다. 로드 밸런서에 대한 액세스 로깅을 활성화 한 후 Elastic Load Balancing은 로그를 캡처하여 압축 파일로 지정한 Amazon S3 버킷에 저장합니다. 언제든지 액세스 로깅을 비활성화 할 수 있습니다.