RDS
RDS
Features
- provides Relational Database service
- supports MySQL, MariaDB, PostgreSQL, Oracle, MSSQL Server, MySQL-compatible Amazon Aurora DB engine
- it is a managed service, shell(root SSH) access is NOT provided
- manages backups, software patching, automatic failure detection, recovery
- supports user initiated manual backups and snapshots
- daily automated backups with database transaction logs enables Point in Time recovery up to the last 5 minutes of database usage
- Snapshots : user-initiated storage volume snapshot of DB instance, backing up the entire DB instance and not just individual databases that can be restored as a independent RDS instance
- max backup retention period : 35 days
- Encryption : support encryption at rest using KMS as well as encryption in transit using SSL endpoints
- For encrypted database : logs, snapshots, backups, read replicas are all encrypted as well
- RDS does not support all features of underlying databases, and if required the database instance can be launched on an EC2 instance
- RMAN(Recovery Manaber) can be used for Oracles backup and recovery when running on an EC2 instance
Multi-AZ deployment
- provides high availability and automatic failover support and is NOT a scaling solution
- maintains a synchronous standby replica in a different AZ
- transaction success is returned only if the commit is successful BOTH on the primary and the standby DB
- Oracle, PostgreSQL, MySQL, MariaDB DB instances use Amazon technology, while SQL Server DB instance use SQL Server Mirroring
- Snapshots and Backups are taken from standby & eliminate I/O freezes
- single AZ RDS : I/O may be briefly suspended while the backup process initializes (typically under a few seconds), and you may experience a brief period of elevated latency.
- During automatic failover, its seamless and RDS switches to the standby instance and updates the DNS record to point to standby
- failover can be forced with the Reboot with failover option
Read Replicas
- uses the PostgreSQL, MySQL, MariaDB DB engines’ built-in replication functionally to create a separate Read Only instance
- updates are asynchrously copied to the Read Replica
- can help scale applications and reduce read only load
- requires automative backups enabled
- replicates ALL databases in the source DB instance
- for Disaster Recovery, can be promoted to a full fledged database
- can be created in a different region for MySQL, Postgres, MariaDB for Disaster Recovery, Migration, Low Latency across regions.
Features
- OLTP (cf. DynamoDB:NoSQL, Redshift:OLAP, Elasticache:Memcached/Redis)
- RDS runs on VM
- You cannot SSH log in to these operation systmes however.(Amazon’s responsibility)
- RDS is NOT Serverless
- Aurora is Serverless
- Error node : the response from RDS API to check RDS for an error
RDS DB Instance Storage
- DB instances use Amazon Elastic Block Store (Amazon EBS) volumes for database and log storage.
- Provisioned IOPS (SSD) storage : if you use online transaction processing in your production environment. for I/O-intensive, transactional (OLTP) database workloads
- RDS Provisioned IOPS storage with MSSQL Server ) RDS volume 16TB
- General Purpose (SSD) storage
Backups, Multi-AZ, Read Replicas
- Backup
- Automated Backups (by default)
- Database Snapshot
- single AZ RDS : I/O may be briefly suspended while the backup process initializes (typically under a few seconds), and you may experience a brief period of elevated latency.
- Read Replicas
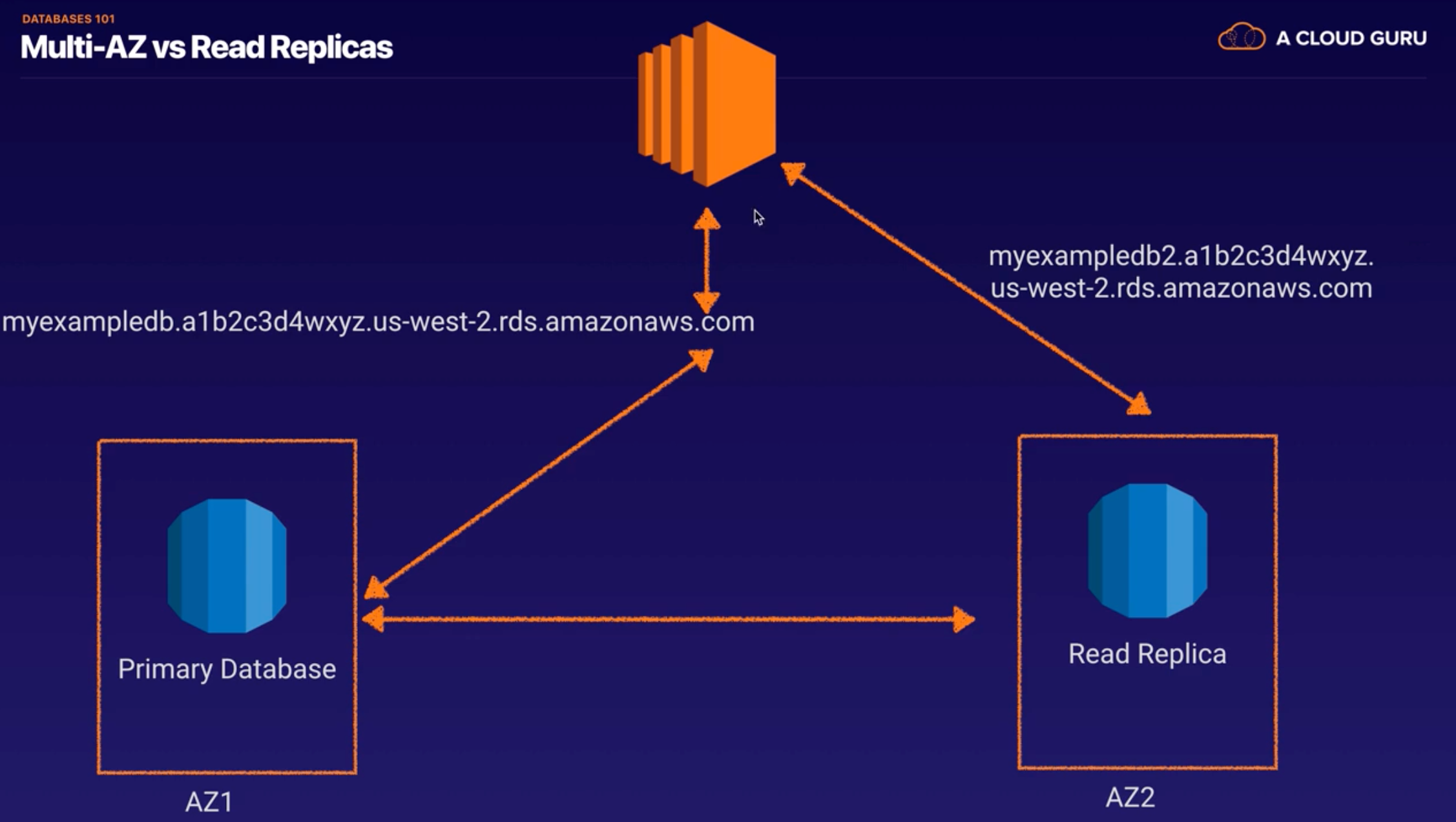
- Can be Multi-AZ, different regions
- Used to increase performance (ex.for heavy traffics)
- Must have backups turned on
- Can be promoted to master, this will break the Read Replica
- data transfer charge when replicating data from primary RDS to secondary RDS is free
- Multi-AZ
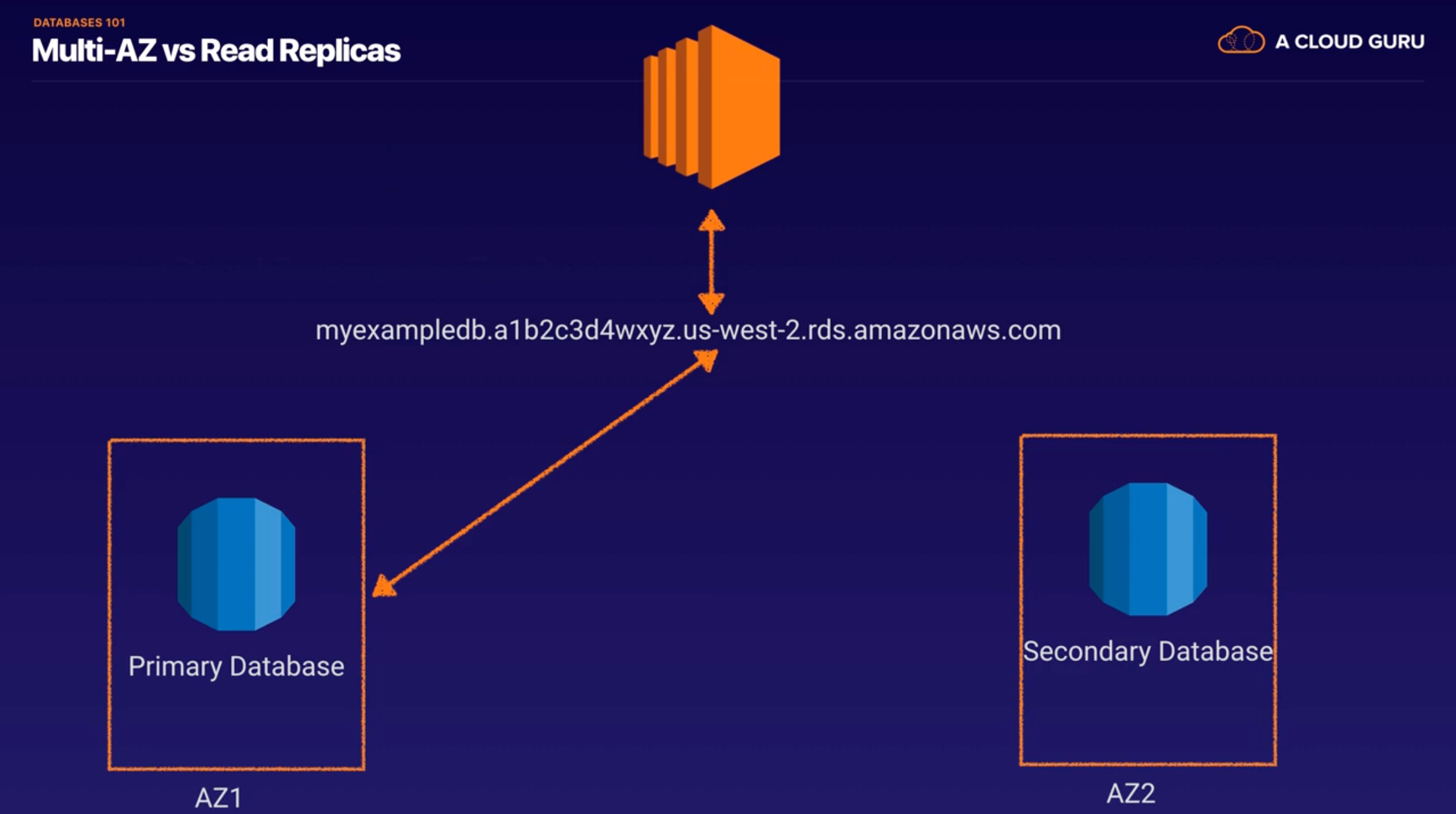
- Used For Disaster Recovery(failover by rebooting RDS instance)
Scenario
- You are deploying an Interactive Voice Response (IVR) telephony system in your cloud architecture that interacts with callers, gathers information, and routes calls to the appropriate recipients in your company. The system will be composed of an Auto Scaling group of EC2 instances, an Application Load Balancer, and a MySQL RDS instance in a Multi-AZ Deployments configuration. To protect the confidential data of your customers, you have to ensure that your RDS database can only be accessed using the profile credentials specific to your EC2 instances via an authentication token.
As the Solutions Architect of the company, which of the following should you do to meet the above requirement?- A) Enable the IAM DB Authentication
- IAM database authentication works with MySQL and PostgreSQL. With this authentication method, you don’t need to use a password when you connect to a DB instance. Instead, you use an authentication token.
An authentication token is a unique string of characters that Amazon RDS generates on request. You don’t need to store user credentials in the database, because authentication is managed externally using IAM.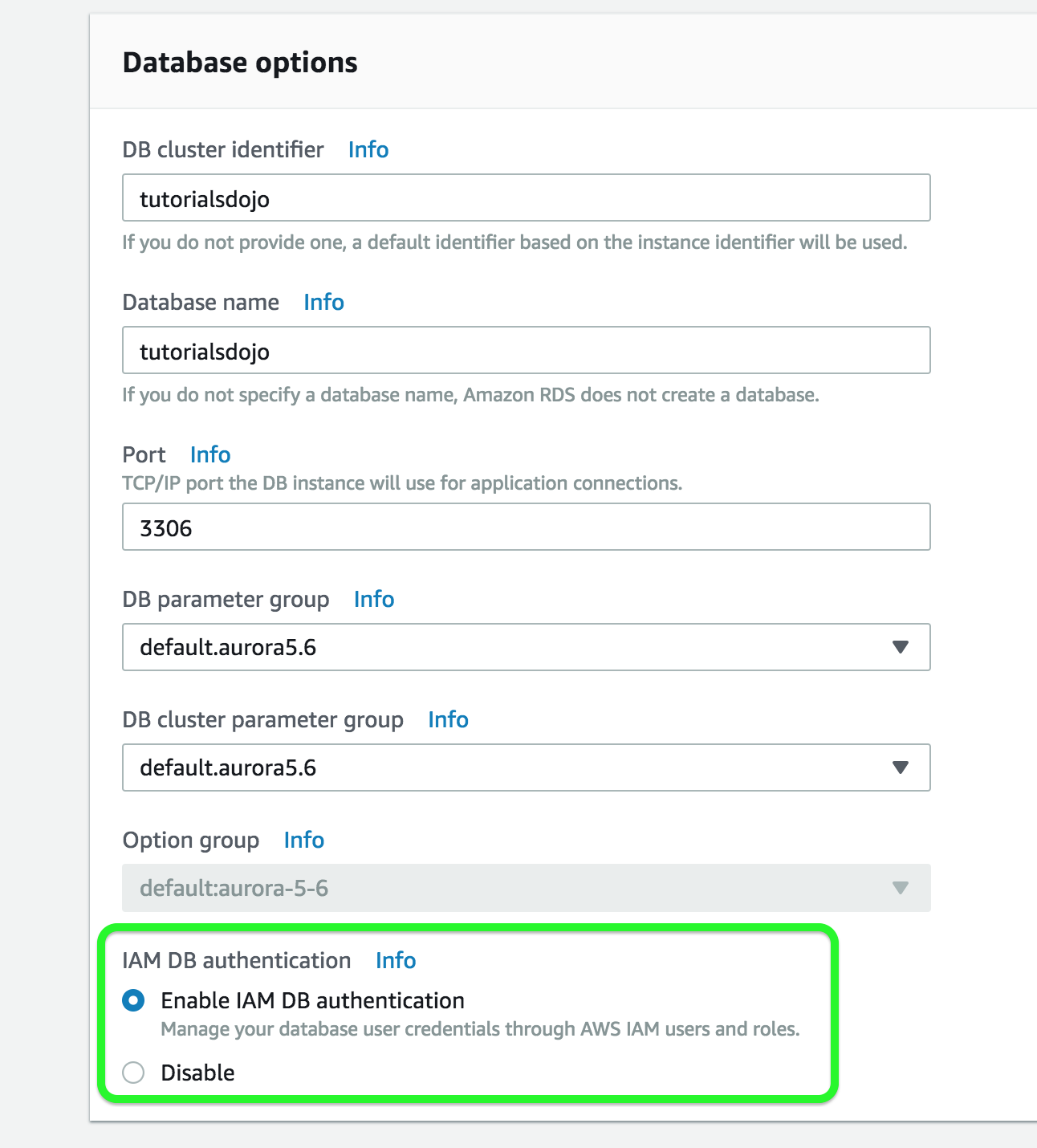
- Configuring SSL in your application to encrypt the database connection to RDS : is incorrect because an SSL connection is not using an authentication token from IAM.
- assigning IAM Role to your EC2 instances which will grant exclusive access to your RDS instance : is incorrect because although you can create and assign an IAM Role to your EC2 instances, you still need to configure your RDS to use IAM DB Authentication.
- a combination of IAM and STS : is incorrect. Although STS is used to send temporary tokens for authentication, this is not a compatible use case for RDS.
- An online cryptocurrency exchange platform is hosted in AWS which uses ECS Cluster and RDS in Multi-AZ Deployments configuration. The application is heavily using the RDS instance to process complex read and write database operations.
To maintain the reliability, availability, and performance of your systems, you have to closely monitor how the different processes or threads on a DB instance use the CPU, including the percentage of the CPU bandwidth and total memory consumed by each process.
Which of the following is the most suitable solution to properly monitor your database?- A) Enable Enhanced Monitoring in RDS
- Enhanced Monitoring metrics are useful when you want to see how different processes or threads on a DB instance use the CPU.
- CloudWatch : although you can use this to monitor the CPU Utilization of your database instance, it does not provide the percentage of the CPU bandwidth and total memory consumed by each database process in your RDS instance.
- CloudWatch Metrics vs. Enhanced Monitoring Metrics
- CloudWatch gathers metrics about CPU utilization from the hypervisor for a DB instance. hypervisor layer performs a small amount of work. The data provided by CloudWatch is not as detailed as compared with the Enhanced Monitoring feature in RDS. Take note as well that you do not have direct access to the instances/servers of your RDS database instance, unlike with your EC2 instances where you can install a CloudWatch agent or a custom script to get CPU and memory utilization of your instance.
- Enhanced Monitoring gathers its metrics from an agent on the instance
- There are a lot of outages in the Availability Zone of your RDS database instance to the point that you have lost access to the database. What could you do to prevent losing access to your database in case that this event happens again?
- A) Enabled Multi-AZ failover
- RDS Multi-AZ deployments : When you provision a Multi-AZ DB Instance, Amazon RDS automatically creates a primary DB Instance and synchronously replicates the data to a standby instance in a different Availability Zone (AZ). Each AZ runs on its own physically distinct, independent infrastructure, and is engineered to be highly reliable.
In case of an infrastructure failure, Amazon RDS performs an automatic failover to the standby (or to a read replica in the case of Amazon Aurora), so that you can resume database operations as soon as the failover is complete. - Snapshot : is incorrect. it does not provide immediate availability in case of AZ failure.
- Read replica : is incorrect because this simply provides enhanced performance for read-heavy database workloads. Although you can promote a read replica, its asynchronous replication might not provide you the latest version of your database.
- An application that records weather data every minute is deployed in a fleet of Spot EC2 instances and uses a MySQL RDS database instance. Currently, there is only one RDS instance running in one Availability Zone. You plan to improve the database to ensure high availability by synchronous data replication to another RDS instance.
Which of the following performs synchronous data replication in RDS?- A) RDS DB instance running as a Multi-AZ deployment
- Multi-AZ Deployment vs. Read Replicas
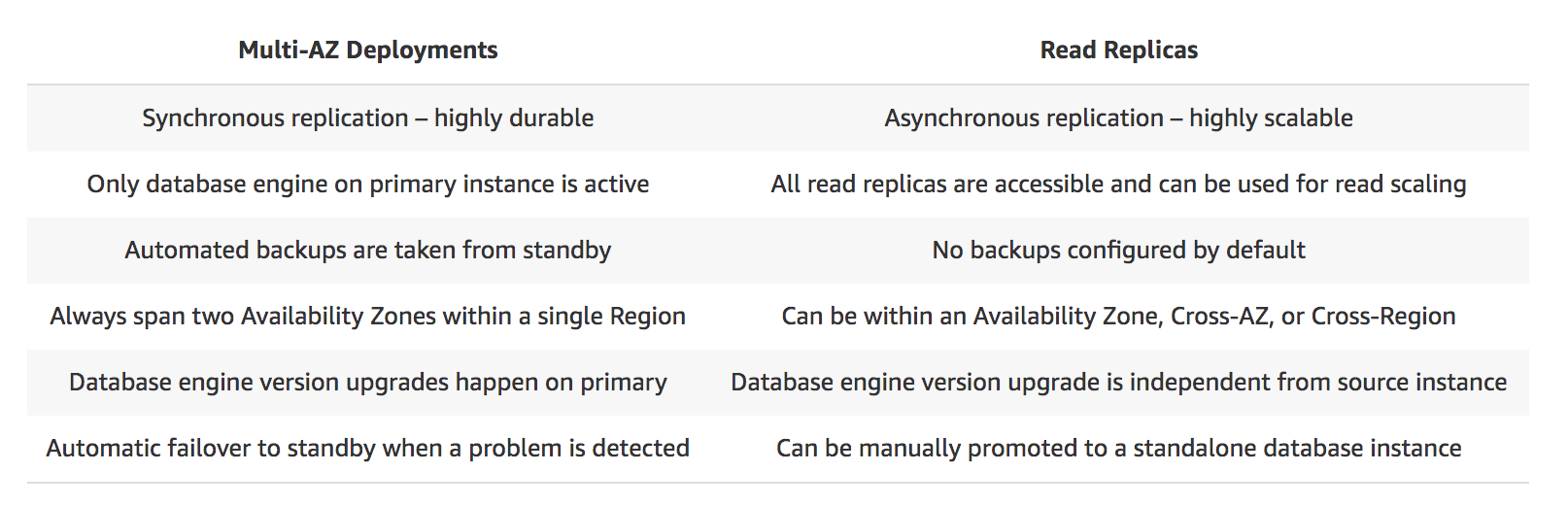
- A Forex trading platform, which frequently processes and stores global financial data every minute, is hosted in your on-premises data center and uses an Oracle database. Due to a recent cooling problem in their data center, the company urgently needs to migrate their infrastructure to AWS to improve the performance of their applications. As the Solutions Architect, you are responsible in ensuring that the database is properly migrated and should remain available in case of database server failure in the future.
Which of the following is the most suitable solution to meet the requirement?- A) creating an Oracle database in RDS with Multi-AZ deployments
- Amazon RDS Multi-AZ deployments provide enhanced availability and durability for Database (DB) Instances, making them a natural fit for production database workloads. When you provision a Multi-AZ DB Instance, Amazon RDS automatically creates a primary DB Instance and synchronously replicates the data to a standby instance in a different Availability Zone (AZ). Each AZ runs on its own physically distinct, independent infrastructure, and is engineered to be highly reliable.
- Launching an Oracle database instance in RDS with Recovery Manager (RMAN) enabled and launching an Oracle Real Application Clusters (RAC) in RDS : are incorrect because Oracle RMAN and RAC are not supported in RDS.
- Migrating your Oracle data to Amazon Aurora by converting the database schema using AWS Schema Conversion Tool and AWS Database Migration Service : is incorrect because although this solution is feasible, it takes time to migrate your Oracle database to Aurora which is not acceptable. Based on this option, the Aurora database does not have a Read Replica and is not configured as an Amazon Aurora DB cluster, which could have improved the availability of the database.
- An accounting application uses an RDS database configured with Multi-AZ deployments to improve availability. What would happen to RDS if the primary database instance fails?
- A) The canonical name record(CNAME) is switched from the primary to standby instance.
- When failing over, Amazon RDS simply flips the canonical name record (CNAME) for your DB instance to point at the standby, which is in turn promoted to become the new primary.
- The IP address of the primary DB instance is switched to the standby DB instance : is incorrect since IP addresses are per subnet, and subnets cannot span multiple AZs.
- An online events registration system is hosted in AWS and uses ECS to host its front-end tier and a Multi-AZ RDS for its database tier, which also has a standby replica. What are the events that will make Amazon RDS automatically perform a failover to the standby replica? (Choose 2)
- A1) Storage failure on primary
- A2) Loss of availability in primary Availability Zone
- Loss of network connectivity to primary
- Compute unit failure on primary
- You are working for an insurance firm as their Senior Solutions Architect. The firm has an application which processes thousands of customer data stored in an Amazon MySQL database with Multi-AZ deployments configuration for high availability in case of downtime. For the past few days, you noticed an increasing trend of read and write operations, which is increasing the latency of the queries to your database. You are planning to use the standby database instance to balance the read and write operations from the primary instance.
When running your primary Amazon RDS Instance as a Multi-AZ deployment, can you use the standby instance for read and write operations?- A) No
- The standby instance will not perform any read and write operations while the primary instance is running.
- Due to the large volume of query requests, the database performance of an online reporting application significantly slowed down. The Solutions Architect is trying to convince her client to use Amazon RDS Read Replica for their application instead of setting up a Multi-AZ Deployments configuration.
What are two benefits of using Read Replicas over Multi-AZ that the Architect should point out? (Choose 2)- A1) It elastically scales out beyond the capacity constraints of a single DB instance for read-heavy database workloads.
- A2) Provides asynchronous replication and improves the performance of the primary database by taking read-heacy database workloads from it.
- Provides synchronous replication and automatic failover in the case of Availability Zone service failures : is incorrect as this is a benefit of Multi-AZ and not of a Read Replica.
- It enhances the read performance of your primary database by increasing its IOPS and accelerates its query processing via AWS Global Accelerator : is incorrect. AWS Global Accelerator is a networking service, not related to RDS, that direct user traffic to the nearest application endpoint to the client, thus reducing internet latency and jitter. It simply routes the traffic to the closest edge location via Anycast.
- A company has an OLTP (Online Transactional Processing) application that is hosted in an Amazon ECS cluster using the Fargate launch type. It has an Amazon RDS database that stores data of its production website. The Data Analytics team needs to run queries against the database to track and audit all user transactions. These query operations against the production database must not impact application performance in any way.
Which of the following is the MOST suitable and cost-effective solution that you should implement?- A) Set up a new Amazon RDS Read Replica of the production database. Direct the Data Analyitcs team to query the production data from the replica.
- You are managing a global news website which is deployed to AWS and is using MySQL RDS. The website has millions of viewers from all over the world which means that the website has read-heavy database workloads. All database transactions must be ACID compliant to ensure data integrity.
In this scenario, which of the following is the best option to use to increase the read throughput on the MySQL database?- A) Enable Amazon RDS replicas
- 읽기 중심의 데이터베이스 워크로드를 위해 단일 DB 인스턴스의 컴퓨팅 파워 또는 I/O 용량을 확장합니다. 이 과도한 읽기 트래픽을 하나 이상의 읽기 전용 복제본으로 이동할 수 있습니다.
- You are working as a Junior Solutions Architect where you are responsible in enhancing the availability and durability of the database instances in your VPC. Your company has a Multi-AZ RDS instance in the ap-northeast-1 region. If a storage volume on the primary instance fails in a Multi-AZ deployment, Amazon RDS automatically initiates a failover to the up-to-date standby instance.
In case of a failover, which record in Route 53 is changed?- A) CNAME
- 장애 조치 시, Amazon RDS는 DB 인스턴스의 정식 이름 레코드(CNAME)가 예비 복제본을 가리키도록 변경합니다. 그러면 이 예비 복제본이 승격되어 새 기본 복제본이 됩니다.
- You are working for a large financial company. In their enterprise application, they want to apply a group of database-specific settings to their Relational Database Instances.
Which of the following options can be used to easily apply the settings in one go for all of the Relational database instances?- A) Parameter Groups
- 데이터베이스 파라미터 그룹(DB 파라미터그룹)은 하나 이상의 DB 인스턴스에 적용 가능한 엔진 설정값의 “컨테이너” 역할을 합니다. DB 파라미터 그룹을 지정하지 않고 DB 인스턴스를 만드는 경우 기본 DB 파라미터 그룹이 사용됩니다. 이 기본값 그룹에는 실행하는 DB 인스턴스에 최적화된 엔진 기본값과 Amazon RDS 시스템 기본 값이 포함됩니다. 그러나 사용자 지정 엔진 설정값을 사용해 DB 인스턴스를 실행하려면 새 DB 파라미터 그룹을 만들고, 필요한 파라미터를 수정하고, 새 DB 파라미터 그룹을 사용하기 위해 DB 인스턴스를 수정하기만 하면 됩니다. 연결이 이루어지면 특정 DB 파라미터 그룹을 사용하는 모든 DB 인스턴스가 해당 DB 파라미터 그룹에 대한 모든 파라미터 업데이트를 가져옵니다.