Route53
Route53 CheatSheet
Features
- Highly available and scalable DNS & Domain Registration Service
- Reliable and cost-effective way to route end users to Internet applications
- Multi-region and backup architectures for High Availability
- ELB is limited to region, does NOT support multi region HA architecture
- supports private Intranet facing DNS service
- Internal resource record sets ONLY work for requests originating from within VPC and currently cannot extend to on-premise
- Global propagation of any changes made to the DN records within 1 min
- Alias resource record set : points to ELB, S3, CloudFront. it is a Route53 extension to DNS. It’s similar to a CNAME resource record set, but supports both for root domain-zone apex ex) example.com for subdomains for ‘www.example.com
- CNAME resource record set : ONLY for subdomains and cannot be mapped to the zone apex record
- Split-view(Split-horizon) DNS : enables you to access in internal version of your website using the same domain name that is used PUBLIC
Routing Policy
- Simple Routing : simple round robin policy
- Weighted round robin : assign weights to resource records sets to specify the proportion ex) 80% : 20%
- Latency Routing : helps improve global applications as request are sent to server from the location with minimal latency, is based on the latency and CANNOT guarantee users from the same geographic will be served from the same location for any compliance reasons
- Geolocation Routing : Specify geographic locations by continent, country, state limited to US, is based on IP accuracy
- Failover Routing : failover to a backup site if the primary site fails and becomes unreachable
- On Failover..
- Active-Active : Weighted, Latency, Geolocation
- Active-Passive : Failover
DNS
- convert ip address to human friendly domain names
- IPv4 vs. IPv6
- Top Level Domains
- .com .gov .gov.au
- IANA(Internet Assigned Numbers Authority) : top level domains are controlled by this in a root zone database
- Domain Registrars : InterNIC, ICANN, WhoIS database
- Common DNS Types : SOA Records, NS Records, A Records, CNAMES, MX Records, PTR Records
- SOR(Start Of Authority Record) : where DNS starts
- NS(Name Server) Records : direct traffic (domain address -> top level domain -> NS Record -> SOA
- A Records : a key to Translate the domain into IP address
- TTL(Time To Live) : the length that a DNS record is cached
- TTL take 48 hours the change takes effect. if you change TTL(1min) cache can be cleared and navigate to another IP)
- CName(Canonical Name) : m.naver.com (give a reference)
- Alias Records
Features
- Route 53 is named because : The DNS Port is on Port 53 and Route53 is a DNS Service
- you will NEVER get an IPv4 addresses for ELB
- Alias Record vs. CNAME : always choose A Record
- A Record : batman -> phonenumber
- CNAME : bruce wayne -> batman (subdomain)
- You can buy domain names directly with AWS
- It can take 3 days to register depending on the circumstances.
- limit of # of domain names : With Route53, 50. However, you can increase by contacting AWS Support
Routing Policies
- Health Checks : you can set health checks on record. if a record fails a health check it will be removed from Route53 until it passes the health check. (you can set SNS notification when fail)
- Simple Routing : pick 1 ip address randomly. you only have 1 record with multiple IP addresses
- Weighted Routing : weight each indivisual record (20% 80%)
- Latency-Based Routing : go to a region which has low latency(the fastest response)
- Failover Routing : active/passive(Primary/Secondary) set up-> Primary health check -> if Primary record set fails(EC2 instance Stop) -> automatic failover
- Geolocation Routing : European Customer -> EU-WEST-1 / US Customer -> US-EAST-1
- Geoproximity Routing(Traffic Flow Only)
- Multivalue Answer Routing : similar to Simple Routing + put health checks on each record set. ex) service effectively creating a form or randomization
Scenarios
- Your company hosts 10 web servers all serving the same web content in AWS. They want Route 53 to serve traffic to random web servers. Which routing policy will meet this requirement, and provide the best resiliency?
- Multivalue Routing
- Multivalue answer routing lets you configure Amazon Route 53 to return multiple values, such as IP addresses for your web servers, in response to DNS queries. Route 53 responds to DNS queries with up to eight healthy records and gives different answers to different DNS resolvers. The choice of which to use is left to the requesting service effectively creating a form or randomization.
- You have a static corporate website hosted in a standard S3 bucket and a new web domain name which was registered using Route 53. You are instructed by your manager to integrate these two services in order to successfully launch their corporate website.
What are the prerequisites when routing traffic using Amazon Route 53 to a website that is hosted in an Amazon S3 Bucket? (Choose 2)- A1) The S3 bucket name must be the same as the domain name
- A2) A registered domain name
- A1) An S3 bucket that is configured to host a static website. The bucket must have the same name as your domain or subdomain. For example, if you want to use the subdomain portal.tutorialsdojo.com, the name of the bucket must be portal.tutorialsdojo.com.
- A2) A registered domain name. You can use Route 53 as your domain registrar, or you can use a different registrar.
- You are an IT Consultant for an advertising company that is currently working on a proof of concept project that automatically provides SEO analytics for their clients. Your company has a VPC in AWS that operates in dual-stack mode in which IPv4 and IPv6 communication is allowed. You deployed the application to an Auto Scaling group of EC2 instances with an Application Load Balancer in front that evenly distributes the incoming traffic. You are ready to go live but you need to point your domain name (tutorialsdojo.com) to the Application Load Balancer. **
In Route 53, which record types will you use to **point the DNS name of the Application Load Balancer? (Choose 2)- A1) Alias with a type “AAAA” record set
- A2) Alias with a type “A” record set
- You have a cryptocurrency exchange portal which is hosted in an Auto Scaling group of EC2 instances behind an Application Load Balancer, and are deployed across multiple AWS regions. Your users can be found all around the globe, but the majority are from Japan and Sweden. Because of the compliance requirements in these two locations, you want your Japanese users to connect to the servers in the ap-northeast-1 Asia Pacific (Tokyo) region, while your Swedish users should be connected to the servers in the eu-west-1 EU (Ireland) region.
Which of the following services would allow you to easily fulfill this requirement?- A) Use Route53 Geolocation Routing Policy
- Setting up a new CloudFront web distribution with the geo-restriction feature enabled : is incorrect because the CloudFront geo-restriction feature is primarily used to prevent users in specific geographic locations from accessing content that you’re distributing through a CloudFront web distribution. It does not let you choose the resources that serve your traffic based on the geographic location of your users.
- You have a new, dynamic web app written in MEAN stack that is going to be launched in the next month. There is a probability that the traffic will be quite high in the first couple of weeks. In the event of a load failure, how can you set up DNS failover to a static website?
- A) Use Route53 with the failover option to a static S3 website bucket or CloudFront distribution
- You are setting up the cloud architecture for an international money transfer service to be deployed in AWS which will have thousands of users around the globe. The service should be available 24/7 to avoid any business disruption and should be resilient enough to handle the outage of an entire AWS region. To meet this requirement, you have deployed your AWS resources to multiple AWS Regions. You need to use Route 53 and configure it to set all of your resources to be available all the time as much as possible. When a resource becomes unavailable, your Route 53 should detect that it’s unhealthy and stop including it when responding to queries.
Which of the following is the most fault tolerant routing configuration that you should use in this scenario?- A) Configure an Active-Active Failover with Weighted routing policy.
- Active-Active Failover
- Use this failover configuration when you want all of your resources to be available the majority of the time. When a resource becomes unavailable, Route 53 can detect that it’s unhealthy and stop including it when responding to queries.
- In active-active failover, all the records that have the same name, the same type (such as A or AAAA), and the same routing policy (such as weighted or latency) are active unless Route 53 considers them unhealthy. Route 53 can respond to a DNS query using any healthy record. Remember that an Active-Active Failover uses all available resources all the time without a primary nor a secondary resource.
- Active-Passive Failover
- Use an active-passive failover configuration when you want a primary resource or group of resources to be available the majority of the time and you want a secondary resource or group of resources to be on standby in case all the primary resources become unavailable. When responding to queries, Route 53 includes only the healthy primary resources. If all the primary resources are unhealthy, Route 53 begins to include only the healthy secondary resources in response to DNS queries.
- A client is hosting their company website on a cluster of web servers that are behind a public-facing load balancer. The client also uses Amazon Route 53 to manage their public DNS.
How should the client configure the DNS zone apex record to point to the load balancer?- A) Create an A record aliased to the load balancer DNS name.
- Route 53의 DNS implementation은 사용자 요청을 Amazon Web Services (AWS) 내부 및 외부에서 실행되는 인프라에 연결합니다. 예를 들어 Elastic Load Balancing 로드 밸런서 뒤의 EC2 인스턴스에서 여러 개의 웹 서버를 실행하는 경우 Route 53은 웹 사이트 (예 : www.tutorialsdojo.com)로 주소 지정된 모든 트래픽을 로드 밸런서 DNS 이름 (예 : elbtutorialsdojo123.elb.amazonaws.com)으로 라우팅합니다.
- 또한 Route 53은 alias 리소스 레코드 세트를 지원하므로 zone apex (예 : tutorialsdojo.com) DNS 이름을 로드 밸런서 DNS 이름에 매핑 할 수 있습니다. 확장 또는 소프트웨어 업데이트로 인해 Elastic Load Balancing과 관련된 IP 주소는 언제든지 변경 될 수 있습니다. Route 53은 로드 밸런서에 대해 하나의 IP 주소로 Alias 리소스 레코드 세트에 대한 각 요청에 응답합니다.
- Creating an A record pointing to the IP address of the load balancer : is incorrect. 로드 밸런서의 IP 주소는 언제든지 변경 될 수 있으므로 로드 밸런서의 DNS 이름을 가리키는 alias record를 사용해야합니다.
- Creating a CNAME record pointing to the load balancer DNS name and creating an alias for CNAME record to the load balancer DNS name : are incorrect. zone apex에 대한 CNAME 레코드를 작성할 수 없습니다. zone apex이라고도하는 DNS 네임 스페이스의 최상위 노드에 alias 레코드를 만들어야합니다. 예를 들어, DNS 이름 tutorialsdojo.com을 등록하면 zone apex는 tutorialsdojo.com입니다. tutorialsdojo.com에 대해 직접 CNAME 레코드를 작성할 수는 없지만, www.tutorialsdojo.com으로 트래픽을 라우팅하는 tutorialsdojo.com에 대한 alias 레코드를 작성할 수 있습니다.
- You are working as a solutions architect for a large financial company. They have a web application hosted in their on-premises infrastructure which they want to migrate to AWS cloud. Your manager had instructed you to ensure that there is no downtime while the migration process is on-going. In order to achieve this, your team had decided to divert 50% of the traffic to the new application in AWS and the other 50% to the application hosted in their on-premises infrastructure. Once the migration is over and the application works with no issues, a full diversion to AWS will be implemented.
Which of the following are the possible solutions that you can implement to satisfy the above requirement? (Select TWO.)- A1) Use Route53 with Weighted routing policy to divert the traffic between the on-premises and AWS-hosted application. Divert 50% of the traffic to the new application in AWS and the other 50% to the application hosted in their on-premises infrastructure.
- A2) Use an Application Elastic Load balancer with Weighted Tartget groups to divert and proportion the traffic between the on-premises and AWS-hosted application. Divert 50% of the traffic to the new application in AWS and the other 50% to the application hosted in their on-premises infrastructure.
- Application Load Balancer로 가중치 대상 그룹을 통한 배포 간소화
- 블루/그린 배포 : 개발자가 온-프레미스에 응용 프로그램을 배포 할 때는 기존 인프라를 새 버전의 응용 프로그램에 재사용해야했습니다. 클라우드에서 개발자는 새로운 버전의 애플리케이션을위한 새로운 인프라를 만듭니다. 이전 버전을 병렬로 실행하여 잠시 동안 분해합니다. 이 기술을 블루 / 그린 배포 라고 합니다 . 두 버전의 앱간에 트래픽을 점진적으로 전환하고 새 버전에서 비즈니스 및 운영 메트릭을 모니터링하고 문제가 발생하는 경우 트래픽을 이전 버전으로 다시 전환 할 수 있습니다.
- Application Load Balancer가 이제 가중치 기반 대상 그룹 라우팅(Weighted Target Groups routing) 을 지원합니다. 이로써 트래픽을 규칙에 따라 여러 대상 그룹으로 전달하는 가중치 기반 라우팅을 수행할 수 있습니다. 따라서 여러 개의 로드 밸런서를 사용할 필요 없이 블루-그린, 카나리아 및 하이브리드 배포와 같은 다양한 사용 사례를 실현할 수 있습니다. 온프레미스와 클라우드 간, 또는 EC2 및 Lambda 등의 서로 다른 컴퓨팅 유형 간에 가동 중지 시간 없는 마이그레이션도 가능합니다.
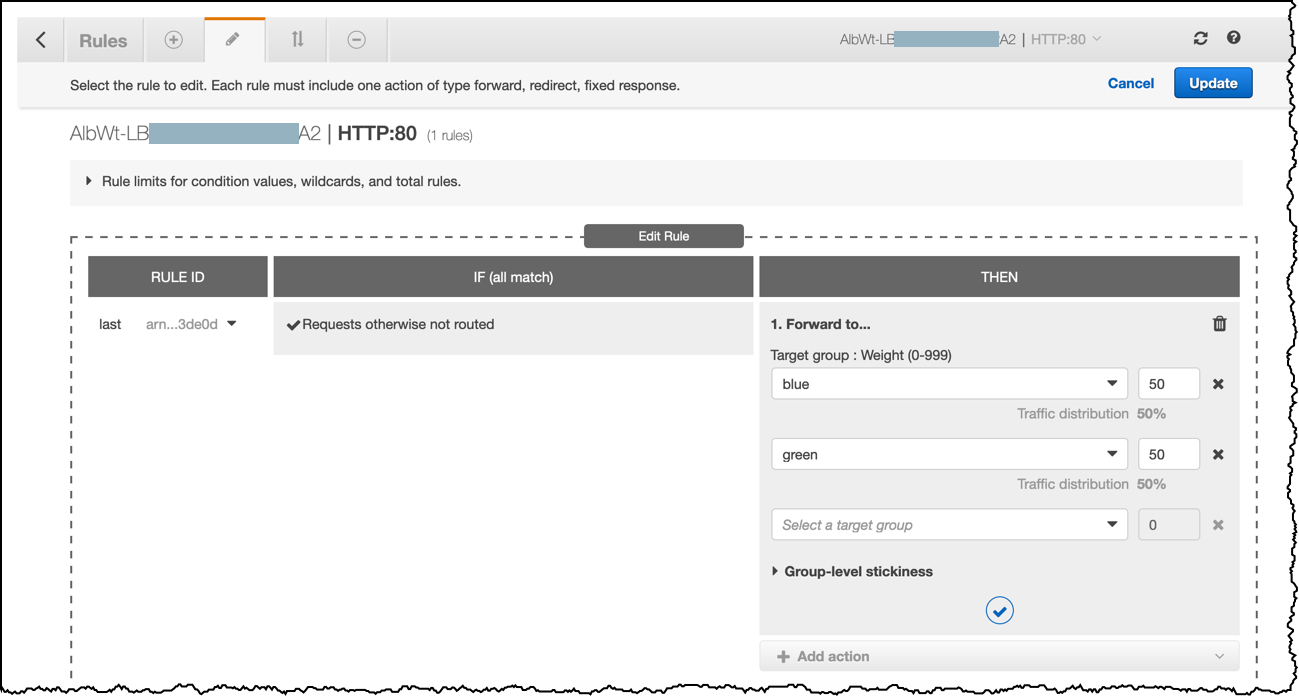
- Route53 가중 라우팅(Weighted routing) 을 사용하면 여러 리소스를 단일 도메인 이름 (tutorialsdojo.com) 또는 하위 도메인 이름 (learn.tutorialsdojo.com)과 연결하고 각 리소스로 라우팅되는 트래픽 양을 선택할 수 있습니다. 이는 로드 밸런싱 및 새로운 버전의 소프트웨어 테스트를 포함하여 다양한 목적에 유용 할 수 있습니다. 가중치를 지정하여 리소스에 할당 될 트래픽 양의 특정 백분율을 설정할 수 있습니다.예를 들어 트래픽의 작은 부분을 한 리소스에 보내고 나머지는 다른 리소스에 보내려면 가중치를 1과 255로 지정할 수 있습니다. 가중치가 1 인 리소스는 트래픽의 1/256 번째를 얻습니다 (1 / 1 + 255)이고 다른 리소스는 255/256 번째 (255 / 1 + 255)를 얻습니다.가중치를 변경하여 저울을 점차적으로 변경할 수 있습니다. 자원으로의 트래픽 전송을 중지하려면 해당 레코드의 가중치를 0으로 변경할 수 있습니다.
- Network Load balancer : doesn’t have Weighted Target Groups to divert the traffic between the on-premises and AWS-hosted application.
- Route 53 with Failover routing : is incorrect. active-passive failover
- AWS Global Accelerator : 를 사용하면 리전별 엔드포인트 그룹에 가중치를 설정할 수 있습니다. 그러면 성능 테스트 또는 애플리케이션 업데이트를 수행할 때 특정 AWS 리전에 대한 트래픽 양을 늘리거나 줄일 수 있습니다. 또한, 상태 저장 애플리케이션이 있는 경우 사용자로부터의 모든 요청을 소스 포트 및 프로토콜과 관계없이 동일한 엔드포인트로 보내어 클라이언트 선호도를 유지할 수 있습니다. 트래픽 다이얼을 사용하여 특정 AWS 리전에 대한 트래픽을 확장 또는 축소할 수 있는 옵션을 제공합니다. 트래픽 다이얼을 사용하면 예를 들어 여러 AWS 리전에 걸쳐 새로운 릴리스에 대한 성능 테스트 또는 블루/그린 배포 테스트를 손쉽게 수행할 수 있습니다 엔드포인트에 장애가 발생하는 경우 AWS Global Accelerator는 사용자 트래픽을 다른 엔드포인트에 할당하여 고가용성을 유지합니다.
- Your manager instructed you to use Route 53 instead of an ELB to load balance the incoming request to your web application. The system is deployed to two EC2 instances to which the traffic needs to be distributed to. You want to set a specific percentage of traffic to go to each instance.
Which routing policy would you use?- A)Weighted